Process management in manufacturing is the systematic approach to designing, monitoring, and optimizing manufacturing processes to enhance efficiency and quality. It encompasses workflow design, resource allocation, and performance measurement to achieve operational excellence. In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, effective process management is vital for streamlining operations, reducing waste, and improving product quality. By implementing robust process management strategies, manufacturers can meet customer demands and swiftly adapt to market changes. This guide explores the fundamentals of process management in manufacturing and its critical role in driving success.
Understanding process management
Process management in manufacturing is a structured approach to planning, executing, monitoring, and optimizing production processes. It ensures that manufacturing operations are efficient, consistent, and aligned with organizational goals. Clear workflows and responsibilities help minimize waste, enhance quality, and boost productivity.
Key components of effective process management include process mapping, standard operating procedures (SOPs), performance metrics, and continuous improvement initiatives. Process mapping provides a visual representation of workflows to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies. SOPs offer detailed task instructions, while performance metrics track key indicators like cycle time and defect rates. Continuous improvement initiatives, such as Lean and Six Sigma methodologies, refine processes over time.
Effective process management streamlines workflows and eliminates redundancies, resulting in faster production cycles and lower operational costs. It also fosters better communication and collaboration among teams, promoting innovation and responsiveness to market demands. Investing in strong process management frameworks helps manufacturers exceed customer expectations and achieve long-term success.
Importance of process management in manufacturing
Effective process management is crucial for enhancing productivity and ensuring quality control. Standardizing workflows and optimizing operations can significantly reduce production time while maintaining high output standards. This leads to fewer defects and greater customer satisfaction, boosting the company’s market reputation.
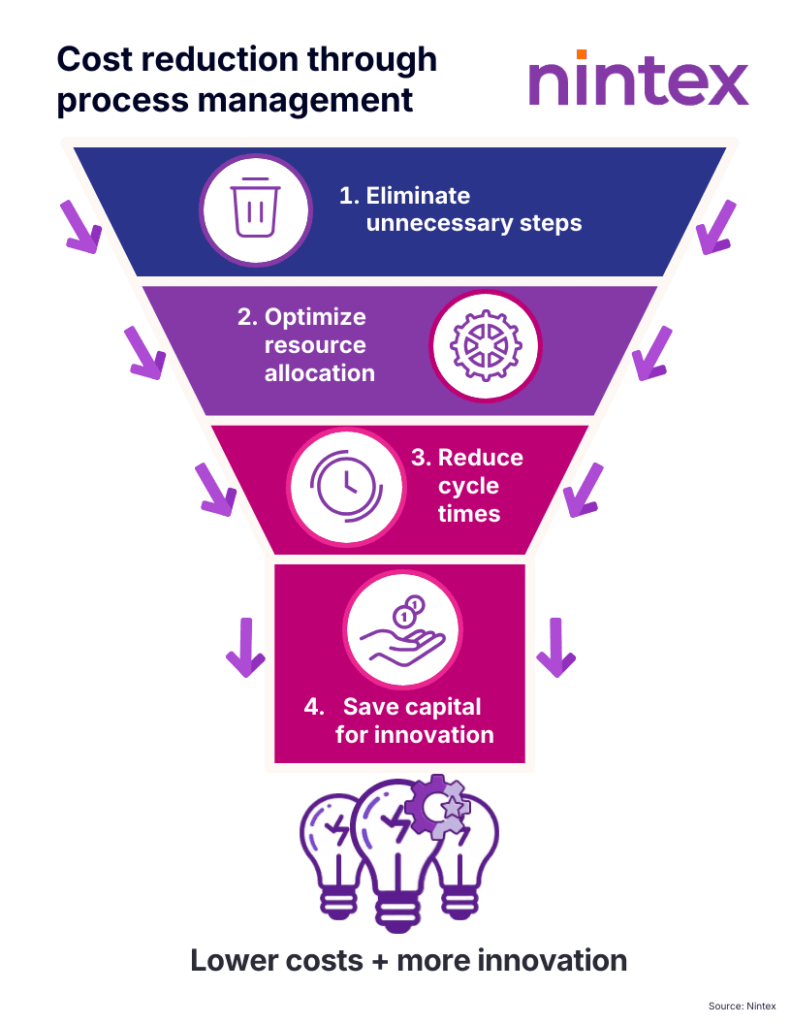
Streamlined processes also contribute to substantial cost reductions. Well-managed processes eliminate unnecessary steps and allocate resources more efficiently, reducing operational costs and freeing up capital for innovation and growth initiatives. Focused process management enables manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing market demands without incurring additional expenses.
Robust process management strengthens compliance and risk management practices. Adhering to industry regulations is essential for maintaining operational integrity and avoiding costly penalties. A well-defined process framework ensures that all operations comply with legal standards and effectively identifies and mitigates potential risks. This proactive approach safeguards the organization and builds trust with stakeholders and customers.
Types of process management in manufacturing
Process management in manufacturing includes various methodologies designed to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve overall quality. Prominent approaches include Lean, Six Sigma, and Agile, each with unique focuses and benefits.
Lean manufacturing prioritizes waste elimination and process optimization, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Six Sigma employs data-driven techniques to reduce defects and variability in processes, leading to increased quality and customer satisfaction. Agile methodology, originally from software development, promotes flexibility and responsiveness to change, enabling teams to adapt quickly to market demands and customer feedback.
In today’s digital landscape, integrating technology is crucial for enhancing process management. Tools such as workflow automation solutions facilitate collaboration, streamline operations, and provide real-time data insights. Technology helps manufacturers implement these methodologies more effectively, driving continuous improvement and operational excellence.
Stages of process management
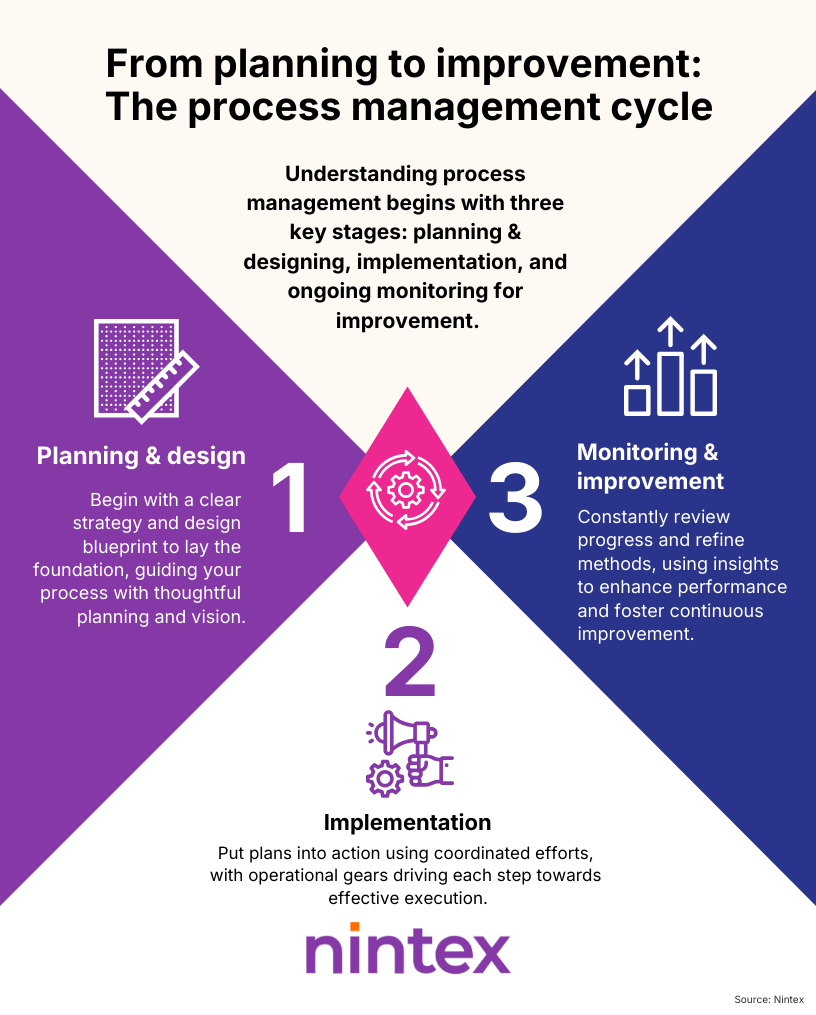
Process management in manufacturing involves several critical stages to ensure efficiency and quality in production. The first stage, planning and designing manufacturing processes, establishes a clear roadmap. This phase includes identifying operational requirements, setting performance benchmarks, and designing workflows that align with business strategy. Effective planning lays the groundwork for streamlined operations, allowing for efficient resource allocation and waste reduction.
The second stage is implementing process management systems. This step translates plans into actionable processes, including deploying technologies and methodologies that enable automation, collaboration, and communication among teams. Integrating process management tools enhances operational visibility, ensuring all stakeholders are aligned and informed throughout the production cycle.
The final stage is monitoring and continuous improvement. Regularly assessing performance metrics and gathering feedback helps identify areas for enhancement and innovation. Continuous improvement methodologies, like Lean and Six Sigma, foster a culture of quality and efficiency. Robust process management systems enable manufacturers to adapt to market changes, optimize workflows, and deliver superior products.
Benefits of effective process management
Effective process management in manufacturing offers numerous benefits that can significantly enhance business performance. One primary advantage is improving operational flexibility. Streamlined processes and data-driven insights allow manufacturers to quickly adapt to changing market demands, optimize resource allocation, and respond to unforeseen challenges. This agility ensures production schedules remain on track and allows companies to pivot swiftly when new opportunities arise.
Effective process management also fosters innovation and responsiveness. Structured workflows help identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement, enabling teams to implement creative solutions. This continuous improvement mindset encourages a culture of innovation, where employees contribute ideas to enhance efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. Companies can stay competitive in an ever-evolving industry landscape.
Moreover, effective process management enhances collaboration across teams. Well-defined and accessible processes improve communication, enabling different departments to work more cohesively. This collaborative environment facilitates knowledge sharing and aligns teams toward common goals, driving productivity and ensuring everyone is on the same page. Breaking down silos and promoting teamwork helps manufacturers harness the full potential of their workforce, leading to superior outcomes and greater success.
Getting started with process management
Implementing process management in manufacturing involves several key steps that drive efficiency and quality. First, map out existing processes to identify areas for improvement. Document workflows, determine bottlenecks, and analyze cycle times. Once the current state is established, set clear objectives for process management, such as reducing waste or improving throughput.
Next, use the right tools and software for process management. Solutions provide a platform for automating workflows, ensuring consistency, and monitoring performance in real-time. With intuitive design capabilities, teams can quickly create process maps, integrate with existing systems, and enforce best practices across the organization.
Training teams effectively is crucial for process management success. Develop a comprehensive training program covering the fundamentals of process management, specific tools being used, and the importance of continuous improvement. Encourage hands-on learning through simulations or workshops and foster a culture of feedback where team members can share insights and suggest enhancements. Investing in training empowers teams to actively participate in refining processes and achieving organizational goals.
Problems and solutions
| Problems | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Inefficient workflows | Process mapping and SOPs |
| High defect rates | Six Sigma methodologies |
| Poor resource allocation | Optimized resource allocation |
| Compliance risks | Adherence to industry regulations |
| High operational costs | Waste elimination and Lean practices |
FAQ
Q. What is process management in manufacturing?
A. Process management in manufacturing involves designing, monitoring, and optimizing manufacturing processes to increase efficiency and quality. It includes workflow design, resource allocation, and performance measurement.
Q. Why is process management important in manufacturing?
A. Effective process management improves productivity, reduces costs, ensures quality control, and enhances compliance and risk management. It helps manufacturers streamline operations and adapt to market changes efficiently.
Q. What are the key components of process management?
A. Key components include process mapping, standard operating procedures (SOPs), performance metrics, and continuous improvement initiatives like Lean and Six Sigma.
Q. How does technology aid process management?
A. Technology, such as workflow automation solutions, facilitates collaboration, streamlines operations, and provides real-time data insights, making process management more effective.
