In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, automating manufacturing processes is essential for companies aiming to improve efficiency and stay competitive. This guide covers the key aspects of manufacturing process automation, including its significance, benefits, and practical steps for implementation. We’ll discuss various automation technologies, address potential challenges, and highlight future trends. Learn how to achieve seamless manufacturing efficiency with effective automation strategies.
What is manufacturing process automation?
Manufacturing process automation involves using technology to streamline and improve production processes, increasing efficiency, reducing errors, and lowering operational costs. This approach integrates machinery, control systems, and information technology to manage production activities with minimal human intervention. By automating repetitive and complex tasks, manufacturers can increase output and overall productivity.
Key components of manufacturing process automation include robotics, sensors, control systems, and software solutions. Robotics handle tasks like assembly, welding, and material handling with precision and speed. Sensors collect real-time data to monitor performance, while control systems enable operators to manage and adjust processes seamlessly. Software solutions automate workflows, ensuring each stage of the manufacturing process is optimized for efficiency.
Compared to traditional manufacturing methods, automation significantly reduces human error and enhances the ability to scale operations quickly. Traditional processes often rely heavily on manual labor, leading to inconsistencies and slower production rates. Automation also allows for better resource management and data analysis, enabling manufacturers to adapt swiftly to market demands and maintain a competitive edge.

Benefits of automating manufacturing processes
Automating manufacturing processes can lead to substantial cost savings and efficiency improvements. By streamlining operations, businesses can reduce labor costs, minimize waste, and optimize resource utilization. Automation technologies help identify bottlenecks and implement changes that boost productivity, resulting in faster production cycles and quicker responses to market demands, ultimately driving profitability.
Automation also enhances quality control and consistency in manufacturing. Automated systems ensure uniform processes, reducing errors associated with manual tasks. With automation solutions, manufacturers can maintain strict quality standards and easily monitor production metrics, leading to higher-quality products that meet customer expectations.
Additionally, automating manufacturing processes improves safety and reduces human error. By minimizing human intervention in hazardous environments, companies can create safer workplaces, decreasing the risk of accidents and injuries. Automation ensures tasks are completed with precision, fostering a culture of safety while maintaining operational efficiency.
Steps to implement manufacturing automation
To implement automation in manufacturing processes, start by assessing your current operations to identify areas with the greatest potential for automation. Review workflows, pinpoint inefficiencies, and determine which repetitive tasks can be streamlined through technology. Understanding your existing processes establishes a solid foundation for automation that targets specific pain points.
Next, set clear goals and objectives for your automation initiatives. Define what you aim to achieve, whether it’s improving productivity, reducing costs, enhancing quality, or increasing flexibility in production. Specific, measurable goals will guide your automation strategy and help evaluate the success of your efforts as you progress.
Choosing the right tools and technologies is crucial for effective automation. Consider solutions that integrate seamlessly with your existing systems and are scalable to meet future needs. Selecting the right tools ensures that your automation efforts are effective and sustainable in the long run.
Types of automation technologies in manufacturing
Automation in manufacturing incorporates various technologies to improve efficiency and productivity. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive tasks by automating them with software robots, reducing human error, increasing speed, and freeing up human resources for more complex tasks. Implementing RPA can significantly enhance operational workflows.
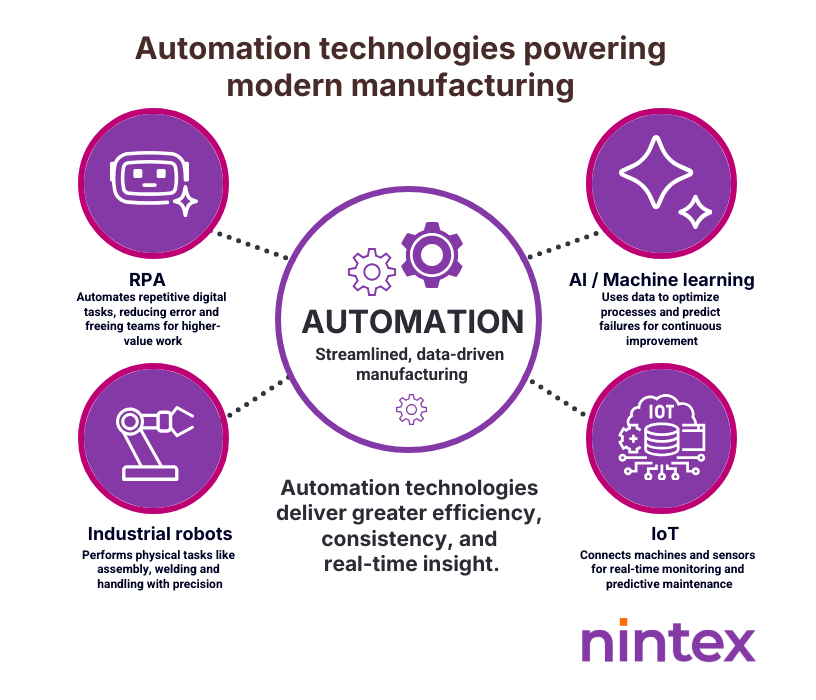
Industrial robots, coupled with machine learning, perform tasks ranging from assembly to quality control. These robots adapt and optimize operations based on real-time data, leading to increased precision and efficiency, allowing manufacturers to respond quickly to production changes.
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized smart manufacturing systems by connecting machines, devices, and sensors. IoT enables real-time monitoring and data collection across production lines, improving decision-making and predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime, and enhancing overall productivity. Together, these technologies create a robust framework for automating manufacturing processes.
Challenges in manufacturing process automation
Automating manufacturing processes can significantly improve productivity, but it also presents challenges. One major issue is the high initial investment costs for automation technology, including equipment, software, and infrastructure upgrades. Companies must evaluate their return on investment to justify these expenses.
Another challenge is integrating new automation solutions with existing systems. Many manufacturing environments rely on a mix of legacy systems that may not easily connect with modern automation technologies. Ensuring seamless communication between these systems is crucial for maintaining operational continuity and achieving efficiency gains.
Change management and employee training are also critical. Transitioning to automated processes can be met with resistance from staff who may be apprehensive about new technologies or concerned about job security. Comprehensive training programs are essential to equip employees with the skills needed to work alongside automated systems effectively. Fostering a culture that embraces change and innovation can help ease the transition and promote a more agile manufacturing environment.
Future trends in manufacturing automation
The landscape of manufacturing automation is rapidly changing, driven by advancements in technology and a growing need for efficiency. One significant trend is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning into manufacturing processes. These technologies enable machines to learn from data and make decisions autonomously, improving production efficiency and reducing downtime. AI-driven systems can optimize operations, predict equipment failures, and adapt to changing market demands with greater agility.
Predictive analytics is also transforming manufacturing operations. By leveraging data from various sources, predictive analytics helps companies forecast trends, manage resources effectively, and improve productivity. This proactive approach allows manufacturers to identify potential bottlenecks and make data-driven decisions to enhance operational efficiency.
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in manufacturing automation. As the global focus shifts towards environmentally friendly practices, manufacturers are seeking ways to automate processes that minimize waste and energy consumption. Integrating sustainable practices meets regulatory requirements and appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. Embracing these trends helps manufacturers remain competitive while contributing to a sustainable future.
Problems and solutions
| Problems | Solutions |
|---|---|
| High initial investment costs | Evaluate return on investment |
| Integration with existing systems | Ensure seamless communication between systems |
| Employee resistance and training | Provide comprehensive training programs |
| Maintaining quality control | Implement automation for consistent quality |
| Ensuring safety in hazardous environments | Minimize human intervention in hazardous tasks |
FAQ
Q. What is manufacturing process automation?
A. It refers to using technology to streamline and improve production processes, increasing efficiency, reducing errors, and lowering operational costs.
Q. What are the key components of manufacturing process automation?
A. Key components include robotics, sensors, control systems, and software solutions.
Q. How does automation compare to traditional manufacturing methods?
A. Automation reduces human error, enhances scalability, and allows for better resource management and data analysis, unlike traditional methods that rely heavily on manual labor.
Q. What are the benefits of automating manufacturing processes?
A. Benefits include cost savings, efficiency improvements, enhanced quality control, improved safety, and reduced human error.
Q. What challenges might arise in automating manufacturing processes?
A. Challenges include high initial investment costs, integration with existing systems, and managing change and employee training.
