In today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment, automating workflows is key to improving efficiency and reducing operational costs. By embracing advanced technologies, organizations can streamline processes, increase productivity, and minimize errors. This guide explores the essentials of manufacturing workflow automation, its benefits, key implementation steps, and common challenges. We will also share real-world success stories and discuss future trends in the industry. Whether you are new to automation or looking to enhance your current processes, this resource will provide the insights you need to optimize your production workflow effectively.
What is manufacturing workflow automation?
Manufacturing workflow automation involves using technology to streamline and enhance manufacturing operations. It aims to boost efficiency, reduce errors, and maintain consistency in production. Key components include process mapping, task automation, real-time monitoring, and data analytics. Integrating these elements creates a cohesive system that accelerates production and improves quality control.
Manual workflows rely on human intervention at various stages, which can introduce variability and increase error risks. In contrast, automated workflows use technology to perform repetitive tasks with precision and speed, freeing human resources to focus on complex problem-solving. This shift not only boosts productivity but also promotes a safer work environment.
Common automation technologies in manufacturing include robotic process automation (RPA), Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and advanced data analytics platforms. These technologies enable real-time data collection and analysis, facilitate machine communication, and support efficient production schedules, significantly improving operational capabilities and reducing costs.
Benefits of automating manufacturing workflows
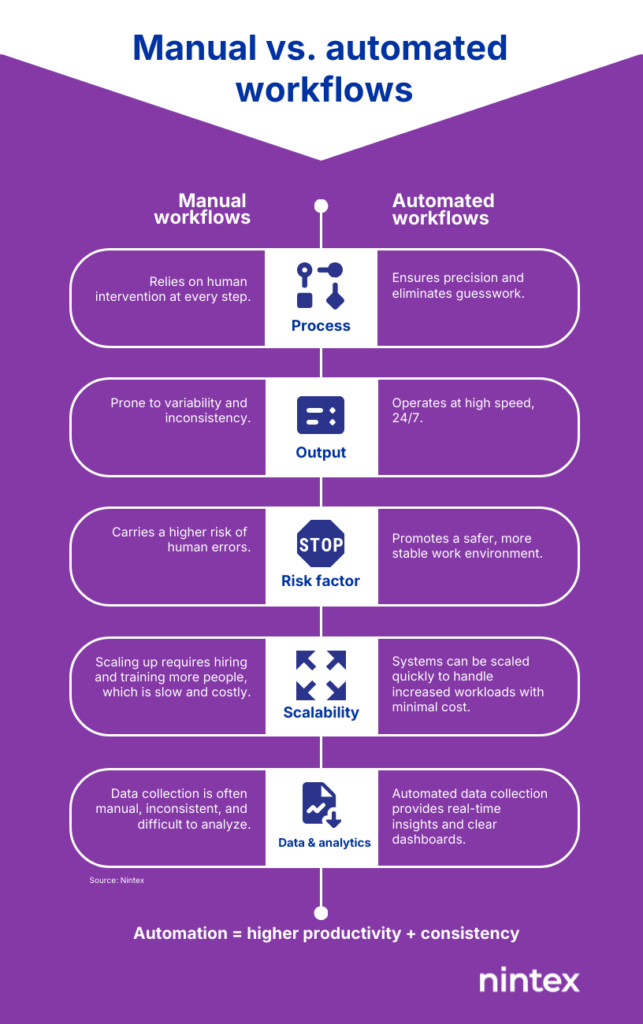
Automating workflows in the manufacturing sector offers several key benefits:
- Increased efficiency and productivity: Automation streamlines processes and eliminates manual tasks, ensuring optimal resource utilization and faster production cycles.
- Reduced errors and waste: Automation minimizes human error and material wastage by standardizing operations, ensuring consistent quality and cost savings.
- Improved compliance and traceability: Automated workflows incorporate checks and balances to ensure adherence to industry regulations and provide robust tracking capabilities for materials and processes, enhancing transparency and accountability.
Key steps to automate your manufacturing workflow
To automate your manufacturing workflow effectively, follow these steps:
- Assess current workflows: Evaluate existing processes to identify areas for automation. Document bottlenecks, redundancies, and manual tasks that could benefit from automation.
- Set clear goals and objectives: Define what success looks like for your organization. Establish measurable goals to guide your automation efforts and track progress.
- Choose the right tools and technologies: Select solutions that integrate with existing systems and offer scalability. Look for powerful automation tools designed specifically for manufacturing workflows, enabling streamlined processes and improved operational efficiency.
Challenges in manufacturing workflow automation
Implementing automation can present several challenges:
- Employee resistance: Employees may fear job displacement. Engage them early, provide training, and highlight the benefits of automation to foster acceptance.
- Lack of technical expertise: Address skill gaps through training programs and hiring experts.
- Integration with existing systems: Ensure new automation technologies are compatible with existing systems to avoid disruptions.
- Data integrity and security: Implement robust data governance practices to protect sensitive information and ensure accuracy.
Real-world examples of successful manufacturing workflow automation
Automation has proven transformative for various industries:
In the automotive sector, a global manufacturer streamlined assembly line processes, reducing delays by 30% and improving delivery timelines. In the electronics industry, a leading manufacturer adopted automation for quality control, standardizing inspections and ensuring compliance, which decreased rework rates by 25%.
These examples highlight the importance of customizing automation solutions to fit specific operational needs. Involving key stakeholders early in the process fosters acceptance and better outcomes.
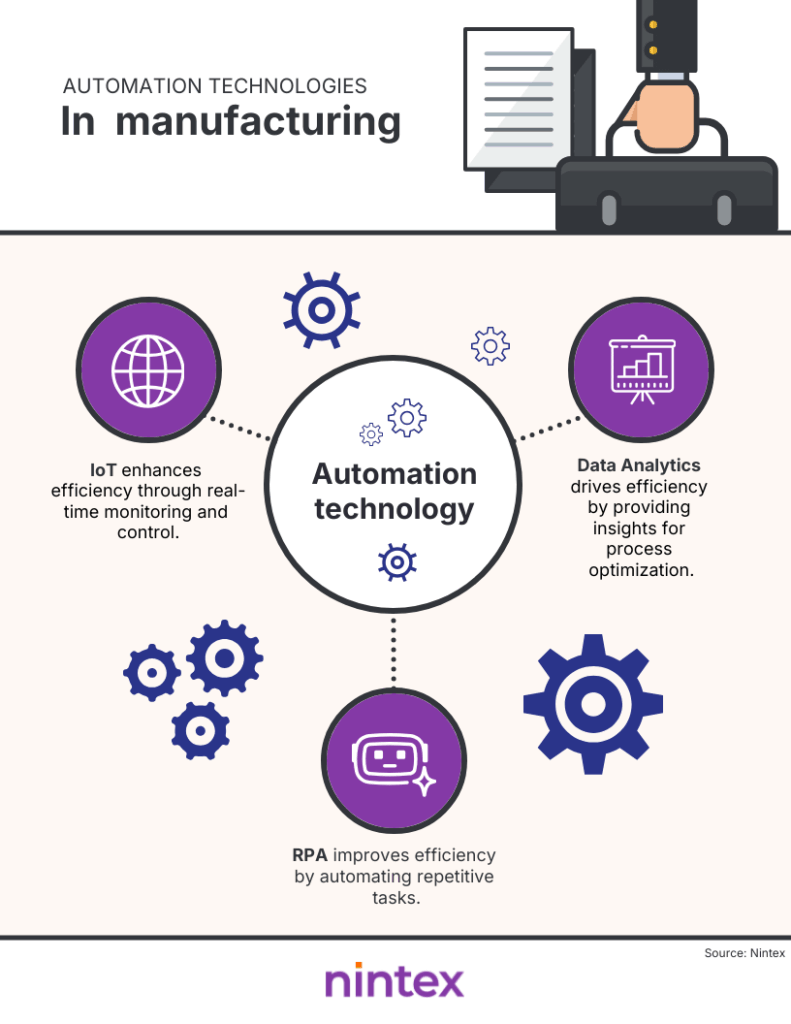
Future trends in manufacturing workflow automation
Emerging technologies are set to revolutionize workflow automation:
- Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and Blockchain: These technologies enable real-time data collection and monitoring, improving decision-making and operations.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI can identify patterns and predict issues, optimizing workflows. ML algorithms adapt to new data, ensuring smarter and more efficient systems.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): These technologies will enhance training and operational efficiency, driving the industry towards innovation and sustainability.
Problems and solutions
| Problems | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Manual task bottlenecks | Automate repetitive tasks |
| High error rates | Standardize processes |
| Compliance challenges | Incorporate automated checks |
| Employee resistance | Engage and train employees |
| Data security risks | Implement robust data governance |
FAQ
Q. What is manufacturing workflow automation?
A. It refers to the use of technology to streamline and improve manufacturing processes, increasing efficiency and reducing errors.
Q. What are the benefits of automating manufacturing workflows?
A. Benefits include increased efficiency, reduced errors and waste, improved compliance, and enhanced traceability.
Q. What are the common challenges in implementing automation?
A. Challenges include employee resistance, lack of technical expertise, integration with existing systems, and data security risks.
Q. What technologies are commonly used in manufacturing automation?
A. Technologies include robotic process automation (RPA), Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and advanced data analytics platforms.
